RAM
Random-access memory (RAM) is a form of computer data storage. Today, it takes the form of integrated circuits that allow stored data to be accessed in any order with a worst case performance of constant time. Strictly speaking, modern types of DRAM are therefore not random access, as data is read in bursts, although the name DRAM / RAM has stuck. RAM is often associated with volatile types of memory, where its stored information is lost if the power is removed. Many other types of non-volatile memory are RAM as well, including most types of ROM and a type of flash memory called NOR-Flash.
Cache
In computer engineering, cache is a component that transparently stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster. The data that is stored within a cache might be values that have been computed earlier or duplicates of original values that are stored elsewhere. If requested data is contained in the cache (cache hit), this request can be served by simply reading the cache, which is comparatively faster. Otherwise (cache miss), the data has to be recomputed or fetched from its original storage location, which is comparatively slower.
ROM
Read-only memory (ROM) is a class of storage medium used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be modified, or can be modified only slowly or with difficulty, so it is mainly used to distribute firmware (software that is very closely tied to specific hardware, and unlikely to need frequent updates).
Flash Memory

Flash memory is a non-volatile computer storage chip that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It is primarily used in memory cards, USB flash drives, MP3 players and solid-state drives for general storage and transfer of data between computers and other digital products. Flash memory costs far less than byte-programmable EEPROM and therefore has become the dominant technology wherever a significant amount of non-volatile, solid state storage is needed. Example applications include PDAs (personal digital assistants), laptop computers, digital audio players, digital cameras and mobile phones. Flash memory is non-volatile, meaning no power is needed to maintain the information stored in the chip.
Graphic Card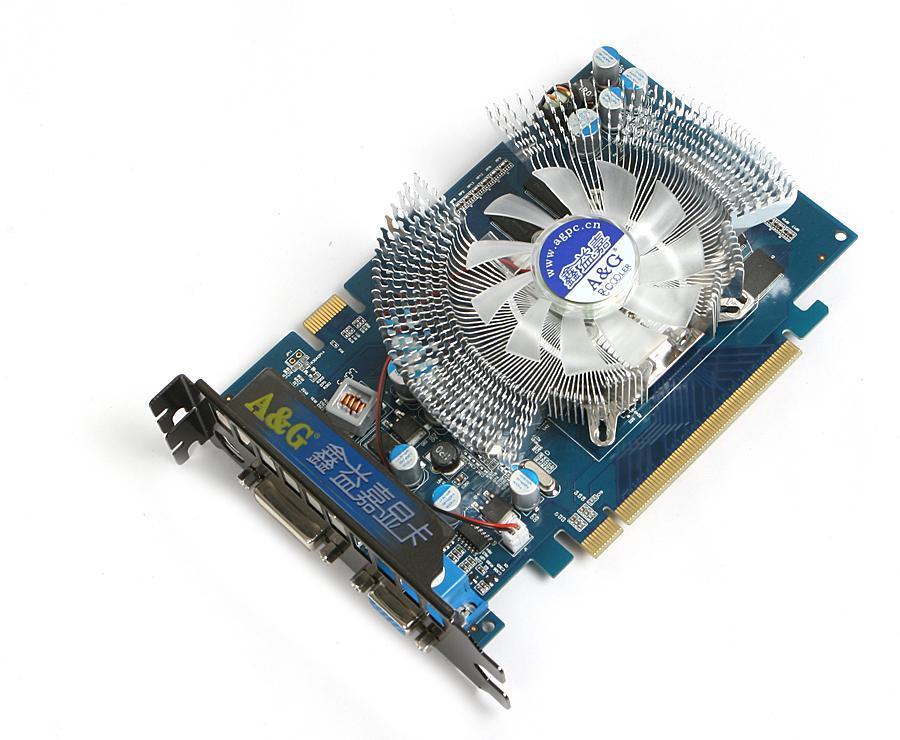
A video card, video adapter, graphics accelerator card, display adapter, or graphics card is an expansion card whose function is to generate output images to a display. Most video cards offer added functions, such as accelerated rendering of 3D scenes and 2D graphics, video capture, TV-tuner adapter, MPEG-2/MPEG-4 decoding, FireWire, light pen, TV output, or the ability to connect multiple monitors (multi-monitor). Other modern high performance video cards are used for more graphically demanding purposes, such as PC games.
Sound Card

A sound card (also known as an audio card) is an internal computer expansion card that facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to external audio interfaces that use software to generate sound, as opposed to using hardware inside the PC. Typical uses of sound cards include providing the audio component for multimedia applications such as music composition, editing video or audio, presentation, education and entertainment (games) and video projection.
Network Interface Card

A network interface controller (also known as a network interface card, network adapter, LAN adapter and by similar terms) is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a compute network. Whereas network interface controllers were commonly implemented on expansion cards that plug into a computer bus, the low cost and ubiquity of the Ethernet standard means that most newer computers have a network interface built into the motherboard.
Plug and Play

In computing, plug and play is a term used to describe the characteristic of a computer bus, or device specification, which facilitates the discovery of a hardware component in a system, without the need for physical device configuration, or user intervention in resolving resource conflicts. Plug and play refers to both the boot-time assignment of device resources, and to hotplug systems.
Universal Serial Bus Port (USB)
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a specification to establish communication between devices and a host controller (usually a personal computer), which has effectively replaced a variety of earlier interfaces such as serial and parallel ports. USB can connect computer peripherals. For many of those devices, USB has become the standard connection method. USB was designed for personal computers, but it has become commonplace on other devices such as smartphones, PDAs and video game consoles, and as a power cord.
Serial Port
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication physical interface through which information transfers in or out one bit at a time (contrast parallel port). Throughout most of the history of personal computers, data transfer through serial ports connected the computer to devices such as terminals and various peripherals.
Modern computers without serial ports may require serial-to-USB converters to allow compatibility with RS 232 serial devices. Serial ports are still used in applications such as industrial automation systems, scientific instruments, shop till systems and some industrial and consumer products.
Parallel Port

A parallel port is a type of interface found on computers (personal and otherwise) for connecting various peripherals. In computing, a parallel port is a parallel communication physical interface. It is also known as a printer port or Centronics port.
Firewire Port

A firewire port is a form of a serial port that is used to transfer data rapidly from one electronic device to another. A similar approach is used when uploading images from a digital camera to a computer hard drive. The FireWire port has the ability to interact with a number of different devices.
Ethernet Port

Ethernet is a family of frame-based computer networking technologies for local area networks (LAN). It defines a number of wiring and signaling standards for the Physical Layer of the standard networking model as well as a common addressing format and a variety of Medium Access Control procedures at the lower part of the Data Link Layer. Most common are Ethernet over twisted pair to connect end systems, and fibe optic versions for site backbones.
High Definition Multimedia Interface

HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a compact audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. HDMI implements the EIA/CEA-861 standards, which define video formats and waveforms, transport of compressed, uncompressed, and LPCM audio, auxiliary data, and implementations of the VESA EDID. HDMI supports, on a single cable, any uncompressed TV or PC video format, including standard, enhanced and high-definition video.
Chapter 9
14 years ago






